Cardiac and respiratory diseases represent some of the most intricate challenges in small-animal veterinary medicine. In dogs and cats, recognition and differentiation of these conditions are a nuanced process, as they often overlap in their clinical presentation.
This article explores the core aspects of diagnosing, managing, and monitoring cardiac and respiratory diseases to help veterinary professionals provide the highest standard of care. It also introduces the reader to an exciting conference and hands-on event, in Orlando, Florida, May 9-11, 2025. In a Heartbeat, It Takes Your Breath Away focuses exclusively on cardiac and respiratory diseases in small animals, offering an unparalleled opportunity to delve into the nuances of recognizing, diagnosing, and managing these conditions.
Recognizing Cardiac and Respiratory Diseases
The ability to recognize these conditions is the cornerstone of effective treatment. While cardiac and respiratory diseases share many clinical signs—such as coughing, dyspnea, lethargy and exercise intolerance—subtle distinctions can help guide the diagnosis.
Cardiac disease often presents with coughing that worsens at night or when the animal is lying down, typically without being triggered by excitement. Syncope, which is usually brief and does not result in complete loss of consciousness, may occur due to arrhythmias or physical exertion. In contrast, respiratory diseases often caused by airway obstruction or inflammation,present with coughing that has a honking quality, worsens with excitement, and may be accompanied by nasal discharge, wheezing or stridor.
Auscultation can offer vital clues for differentiation. Murmurs or arrhythmias are indicative of cardiac disease, while crackles or wheezes are more commonly associated with underlying respiratory conditions. However, overlapping signs can complicate the diagnosis, requiring a mastering of advanced diagnostic strategies.
Diagnostic Tools
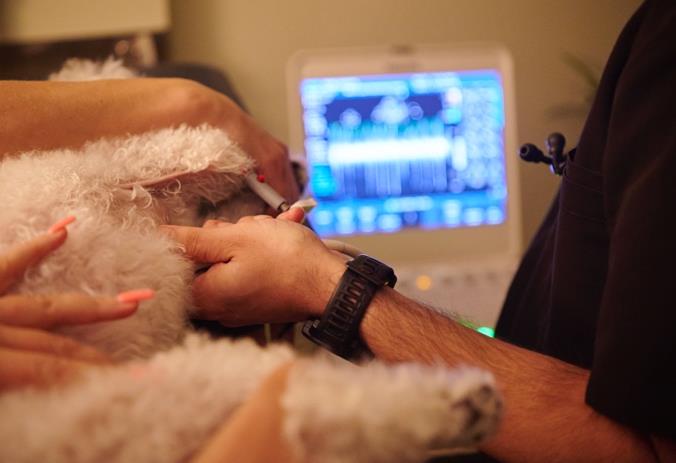
Advanced diagnostics play a pivotal role in confirming the nature and severity of disease. Radiographs are invaluable for assessing heart size, pulmonary vasculature and lung patterns. Echocardiography is indispensable for visualizing cardiac structure and function, aiding in the diagnosis of conditions such as degenerative valve disease, dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and pericardial effusion. Electrocardiography and Holter monitoring are equally critical in ruling out arrhythmias or conduction abnormalities. Blood gas analysis further enhances diagnostic precision by identifying respiratory inefficiencies, such as hypoxemia or hypercapnia, particularly in patients presenting with acute respiratory distress. Mastering these diagnostic tools allows veterinarians to gain confidence and tailor interventions accurately.
Management Strategies
Management strategies for these conditions vary significantly between acute and chronic presentations. In acute cardiac cases, the immediate goal is stabilization. Diuretics such as furosemide are administered to control pulmonary edema, while oxygen therapy alleviates hypoxia. Pimobendan is often used to enhance left ventricular systolic performance. Acute respiratory conditions necessitate similar urgency, with oxygen supplementation being paramount. Bronchodilators such as terbutaline and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation can be critical interventions for primary respiratory conditions.

Chronic management, however, focuses on sustaining long-term stability and improving quality of life. For cardiac diseases, this may involve ACE inhibitors, antiarrhythmics, and dietary interventions. Chronic respiratory cases require anti-inflammatory medications, long-term bronchodilators and weight management to reduce respiratory effort. Whether caused by primary respiratory disease, such as lung fibrosis, or secondary to a severe cardiac condition, clinical signs caused by pulmonary hypertension can be alleviated by sildenafil.
Anesthetic Considerations
Anesthesia in patients with cardiac or respiratory disease poses a significant challenge, demanding a meticulous and tailored approach. Pre-anesthetic evaluations are essential to assess risk and stabilize the patient before the procedure. Drug selection plays a critical role; opioids and benzodiazepines are often preferred for their minimal cardiovascular and respiratory impact, whereas agents such as alpha-2 agonists are avoided due to their potential to exacerbate underlying conditions. During anesthesia, continuous monitoring is imperative, with tools such as ECG, blood pressure monitors, pulse oximetry and capnography providing real-time data to ensure patient safety and optimize outcomes.
Long-Term Monitoring and Collaboration
Ongoing monitoring and collaboration between veterinary professionals are critical for managing these conditions. Continuous evaluation with tools such as Holter monitors and regular echocardiographic assessments is essential for tracking disease progression and tailoring treatment plans. Educating pet owners to recognize early signs of decompensation, such as increased respiratory rate and effort or syncope, empowers them to seek timely veterinary care. Follow-up protocols should be individualized, emphasizing proactive adjustments to therapy as the condition evolves.
Patients presenting with both cardiac and respiratory diseases represent a unique and complex subset, requiring an integrative approach. Prioritization of treatment often depends on which condition is more life-threatening at the time of presentation. Medications such as diuretics and oxygen therapy are often administered when the presentation is unclear and the underlying condition could be primarily cardiac or respiratory. However, ideally early determination of the underlying condition may prevent potential drug interactions or side effects that could exacerbate either condition. Collaborative care involving cardiologists and the primary doctor can significantly enhance outcomes for these patients.

Wet Lab Highlights:
Hands-On Echocardiography
The In a Heartbeat, It Takes Your Breath Away wet lab offers an exceptional opportunity for veterinary professionals to enhance their diagnostic and treatment skills. One of the key highlights is the hands-on echocardiography workshop. Under the guidance of experienced cardiologists and echocardiographers, attendees will gain familiarity and confidence with the echocardiographic technique to differentiate primary cardiac conditions, assess the severity of cardiac dysfunction and enabling them to develop more informed and precise treatment plans. This interactive session will ensure that participants leave with actionable skills they can immediately apply in their practice.
Conclusion
Successfully managing cardiac and respiratory diseases in small animals requires a multifaceted approach that combines clinical expertise with advanced diagnostic and therapeutic tools. By recognizing subtle differences in presentations, employing appropriate diagnostics, and tailoring treatment plans to each patient, veterinary professionals can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for their patients.

With its world-class speakers and hands-on sessions, the In a Heartbeat, It Takes Your Breath Away conference offers a transformative experience for veterinary practitioners at all stages of their careers.
Whether you are a seasoned practitioner or a newly minted veterinarian, this conference will equip you with the confidence and skills to navigate these challenging cases effectively.